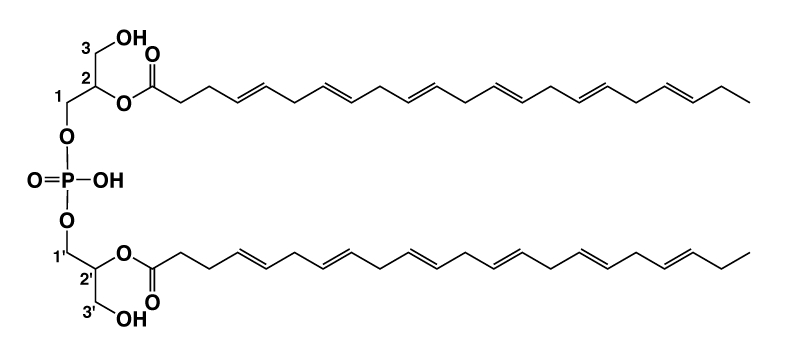
Di-docosahexaenoyl (22:6)-BMP
Di-docosahexaenoyl (22:6)-BMP
Bis(monoacylglycerol)phosphate (BMP) is a unique lysosomal phospholipid that plays important roles in lysosomal degradation pathways. The di-22:6-BMP, a specific species of BMP, is Nextcea’s patented biomarker of lysosomal storage dysfunction for Parkinson’s disease (LRRK2 mutation) diagnostics, drug efficacy assessments, and therapeutic uses. The di-22:6-BMP is measured in urine and plasma/serum to evaluate the impact of LRRK2 kinase inhibitors on lysosomal functions.
Bis(monoacylglycerol)phosphate (BMP)はリソゾームリン脂質の一種で、リソ ゾームの分解経路における重要な役割を担っています。BMPの特有の分子種 di-22:6-BMPは、Nextceaが特許権を持つリソゾーム貯蔵不全の特異的なバイ オマーカーで、パーキンソン病(LRRK2変異)の診断、薬効評価、治療への利用 が考えられます。リソゾーム機能に対するLRRK2キナーゼ阻害剤の効果を評価 するために、尿・血漿/血清中のDi-22:6-BMPを測定します。
In Figure 1, Urine di-22:6-BMP decreased following administration of LRRK2 inhibitors (MLi 2, PFE 360, and GNE-7915) in nonclinical animal studies presented by Michael J Fox Foundation [1][2].
Michael J Fox財団が提供した非臨床動物試験で、LRRK2阻害剤(MLi-2、PFE-360、GNE- 7915)の投与により尿中di-22:6-BMP量の低下が認められました[1][2]。

Figure 1
Figure 1
LRRK2, BMP, and Parkinson’s disease
LRRK2、BMP、パーキンソン病
Parkinson’s disease is linked to mutations in the leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2). These mutations impair endolysosomal/ lysosomal function and are neurotoxic [1][2]. BMP increases with lysosomal dysfunction associated with neurodegenerative diseases, including Parkinson’s disease [3][4]. Decreased BMP is observed in LRRK2 knockout rodents and animals treated with LRRK2 inhibitors, reflecting LRRK2 kinase activity. Di22:6-BMP provides an important tool for researchers to evaluate the effectiveness of new drug candidates to treat idiopathic and genetic forms of Parkinson’s disease (i.e., LRRK2, GBA, and PINK1).
パーキンソン病は、Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2(LRRK2)の変異と関連づけられています 。これらの変異によりエンドリソゾーム/リソゾーム機能が悪化し、神経毒性が生じます[1][2]。 パーキンソン病を含む神経変性疾患に関連したリソゾーム機能不全に伴って、BMPの増加が 認められます[3][4]。LRRK2ノックアウトマウスやLRRK2阻害剤で処理した動物では、LRRK2 キナーゼ活性に反映して、BMPの減少が認められます。Di-22:6-BMPは、新薬候補の薬効 評価を行う研究者たちにとって重要な手段となります。
In Figure 2, urine was collected from healthy donors, idiopathic PD patients, and LRRK2 G2019S mutation carriers with and without PD. Di-22:6-BMP and its 2,2’-di 22:6-BMP isomer were quantitated, with an authentic reference standard and internal standard, by high resolution UPLC-MS/MS. Biomarker concentrations in urine were normalized to urine creatinine. The di-22:6-BMP biomarker and its 2,2’-isomer were each >3-fold higher (p-value ≤0.0001) in LRRK2 G2019S mutation carriers, than non-carriers with and without PD [5].
In Figure 2, urine was collected from healthy donors, idiopathic PD patients, and LRRK2 G2019S mutation carriers with and without PD. Di-22:6-BMP and its 2,2’-di 22:6-BMP isomer were quantitated, with an authentic reference standard and internal standard, by high resolution UPLC-MS/MS. Biomarker concentrations in urine were normalized to urine creatinine. The di-22:6-BMP biomarker and its 2,2’-isomer were each >3-fold higher (p-value ≤0.0001) in LRRK2 G2019S mutation carriers, than non-carriers with and without PD [5].
The BMP biomarker levels in human urine
The BMP biomarker levels in human urine