Kidney Safety

UPLC-MS/MS Biomarker
Assessment
Using our biomarkers, Nextcea provides preemptive insight to drug candidates that may indicate potential kidney toxicity.
Oligonucleotide drugs and antibiotics has been known to cause kidney toxicity, a condition of which over two million patients battle every year. In efforts to guide clinical development, Nextcea is dedicated to the application of drug safety biomarkers that are quantitative, highly specific, and sensitive in order to provide insight into onset, severity, and recovery of toxicities.
Kidney Safety
Protein
Biomarkers
by UPLC-MS/MS
Nextcea measures kidney safety protein biomarkers in urine to assess & pinpoint toxicity in kidney by drug candidates
Sensitive urinary biomarkers are needed to detect kidney injury at the earliest stages. To monitor the onset and time-course of toxicity for pharmaceutical GLP clinical trial studies, Nextcea has developed and validated a proprietary UPLC-MS/MS assay to quantitate our biomarkers simultaneously in a single analysis.
The following proteins are among some of the biomarkers used to assess the risk of overall kidney toxicity. Additionally, with an abundancy of each protein to a specific nephron region, Nextcea is further able to use the correlation to represent and determine the nephron site of which potential kidney toxicity stems from.
Nextcea kidney safety biomarkers and their corresponding nephron region
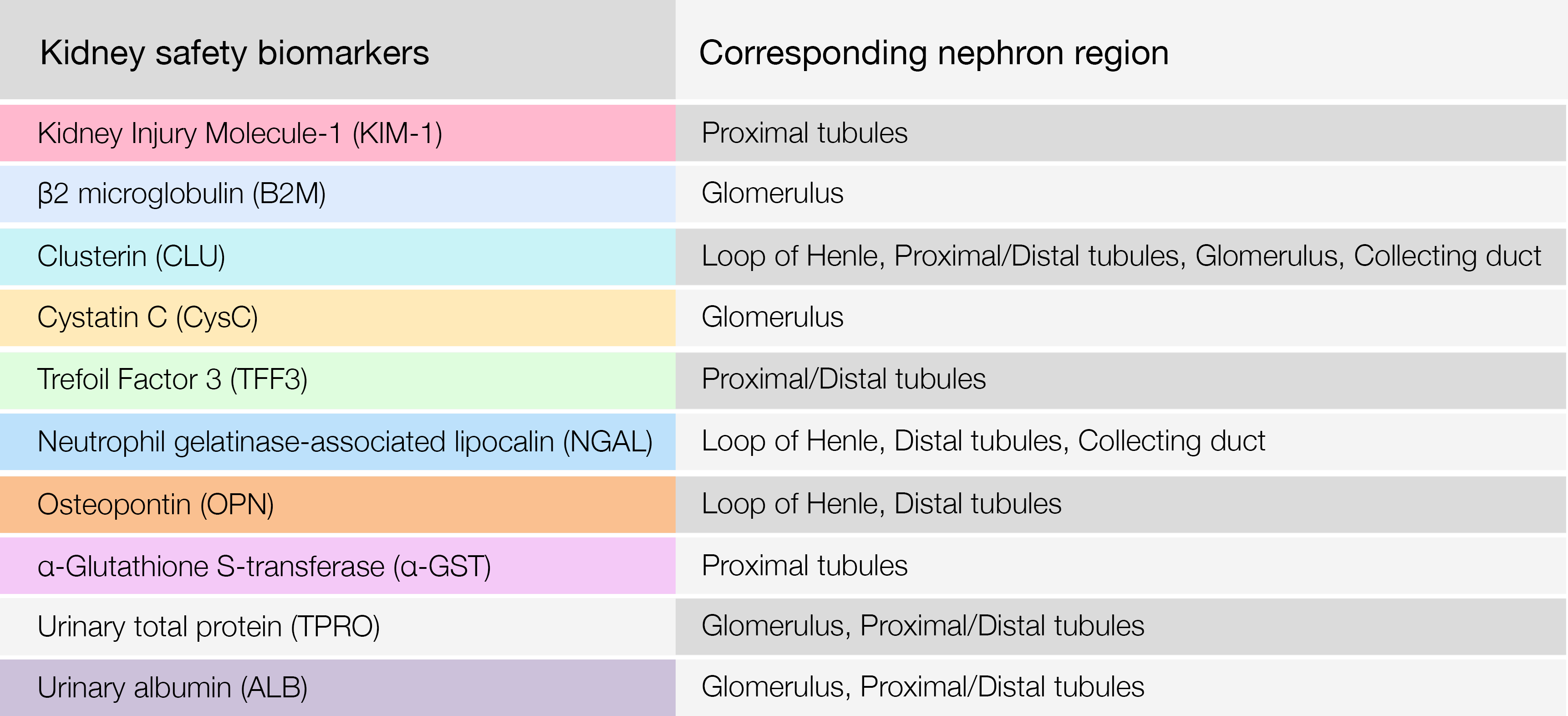
The following assays were performed following treatment by drug candidates in order to determine the risk of kidney toxicity in nephrons such as in Loop of Henle, Glomerulus, or Proximal/Distal Tubules.
Kidney toxicity biomarker levels following treatment of drug candidate Gentamicin in rats
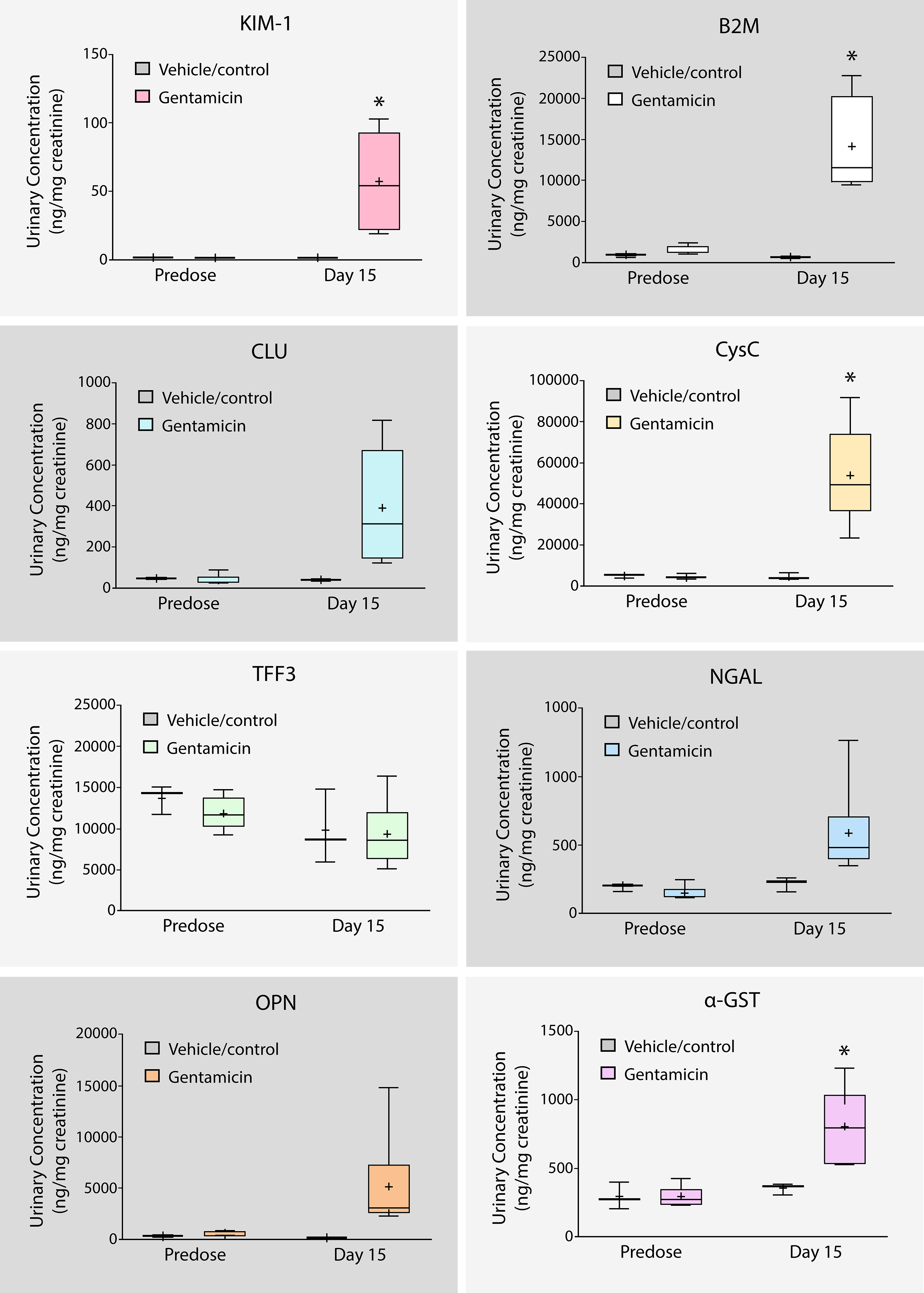
As biomarker levels rise, the indication of kidney toxicity becomes stronger. Conversely, a decrease in biomarker levels indicates a greater likelihood the drug candidate has subverted kidney toxicity. i.e. In Figure 2, following treatment of drug candidate Gentamicin, the rise in the Kim1 biomarker suggests Proximal tubules in nephron will likely to be damaged.
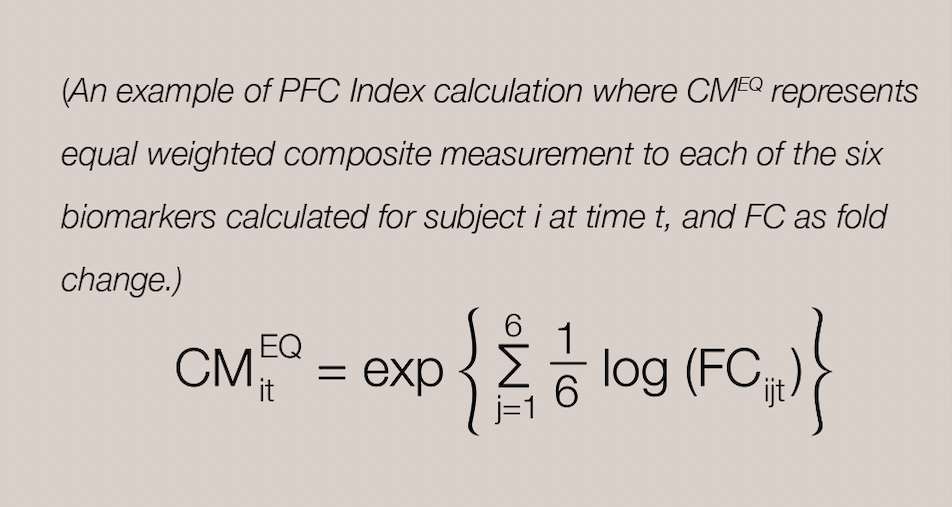
Bringing safety assessment of drug candidates via  recommended PFC Index Integration of the measured protein biomarkers
recommended PFC Index Integration of the measured protein biomarkers
The PFC index is a group geometric mean of the fold changes from baseline of the six urine creatinine (uCr)-normalized urine biomarkers in subjects. (i.e. Six of the biomarkers listed above). A principal component analysis is then performed with the data to simplify and reduce the set of six individual biomarker measurements identified above into a single composite measurement. Nextcea determines the PFC Index for drug candidates, a calculation representing the threshold of pharmaceutical drug toxicity in kidneys.

Nextcea is capable of measuring kidney toxicity protein biomarkers to provide the FDA recommended PFC index, a calculation of the geometric mean or principal component analysis that determines the threshold of pharmaceutical drug toxicity in humans for drug candidates.
References
- Liu N., Tengstrand E., Boernsen O., Bak S., Hsieh F. (2019) Validation of a multiplexed LC–MS/MS clinical assay to quantify insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins in human serum and its application in a clinical study. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 371: 74-83
- Zhou Y, Vaidya V, Brown R, et al. Comparison of Kidney Injury Molecule-1 and Other Nephrotoxicity Biomarkers in Urine and Kidney Following Acute Exposure to Gentamicin, Mercury, and Chromium. Toxicological Sciences 2008;01(1):159–170