Drug-induced Phospholipidosis or similarly called Parkinsonism (DIPL) is a phospholipid storage disorder characterized by an excessive accumulation of multi-lamellar bodies (myeloid bodies) in cells and tissues. Instead of just morphological changes, patients instead will potentially experience an onslaught of clinical toxicities (such as Parkinson’s symptoms), heart irregularities like QT prolongation, or many more afflictions) due to drugs — and in many cases, from anti-depressive drugs. Because DIPL may be linked to unwanted toxicities, its presence may result in the delay or discontinuation of new drug development of non-clinical/clinical studies. DIPL should be carefully evaluated and interpreted on a case-by-case basis, especially for chronically used drugs.
With our proprietary di-22:6-BMP biomarker, Nextcea distinguishes ourselves by quantitating DIPL through LC-MS methods that are:
di-22:6 BMP biomarker excreted from tissues to blood streams and accumulated in urine

Thompson KL, Haskins K, Rosenzweig BA, et al.
Comparison of the diagnostic accuracy of di-22:6-bis(monoacylglycerol) phosphate and other urinary phospholipids for drug-induced phospholipidosis or tissue injury in the rat.
Int J Toxicol. 2012;31(1):14-24. doi:10.1177/1091581811430167

Hsieh F. Tengstrand E.
Drug-induced phospholipidosis assessment from nonlcinical to clinical studies.
Dokusei Shitsumon-Bako 2015, 17: 24-36
Thompson KL, Zhang J, Stewart S, et al.
Comparison of urinary and serum levels of di-22:6-bis(monoacylglycerol) phosphate as noninvasive biomarkers of phospholipidosis in rats.
Toxicol Lett. 2012;213(2):285-291. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2012.07.013


Nextcea aspires to provide regulatory views that answer:
di-22:6-BMP Biomarker
Di-docosahexaenoyl (22:6)-BMP
Bis (monoacylglycerol) phosphate (BMP) is a unique lysosomal phospholipid that plays important roles in lysosomal degradation pathways. BMP is increased in the tissues of animals and humans with DIPL and the lysosomal storage disorders. Elevated di-docosahexaenoyl (22:6)-BMP (a unique isoform of BMP) is Nextcea’s proprietary biomarker, and in plasma and urine, a reliable indicator of tissue DIPL for nonclinical and clinical studies.
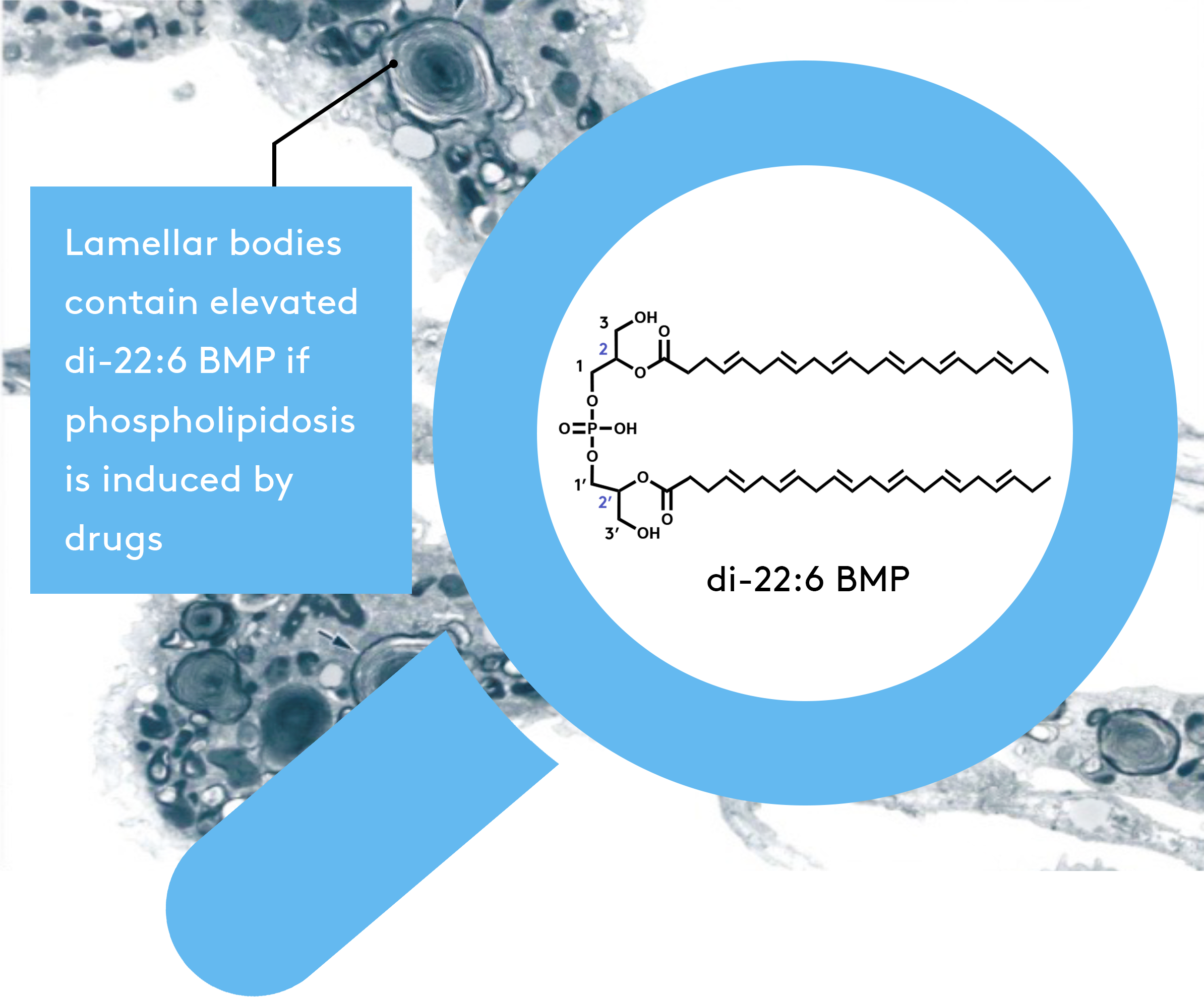
di-22:6 BMP as a validated biomarker to monitor the onset and time course of DIPL
Nextcea has identified our proprietary di-22:6-BMP biomarker as a validated marker of phospholipidosis, with the onset of DIPL containing elevated levels of di-22:6 BMP in urine.
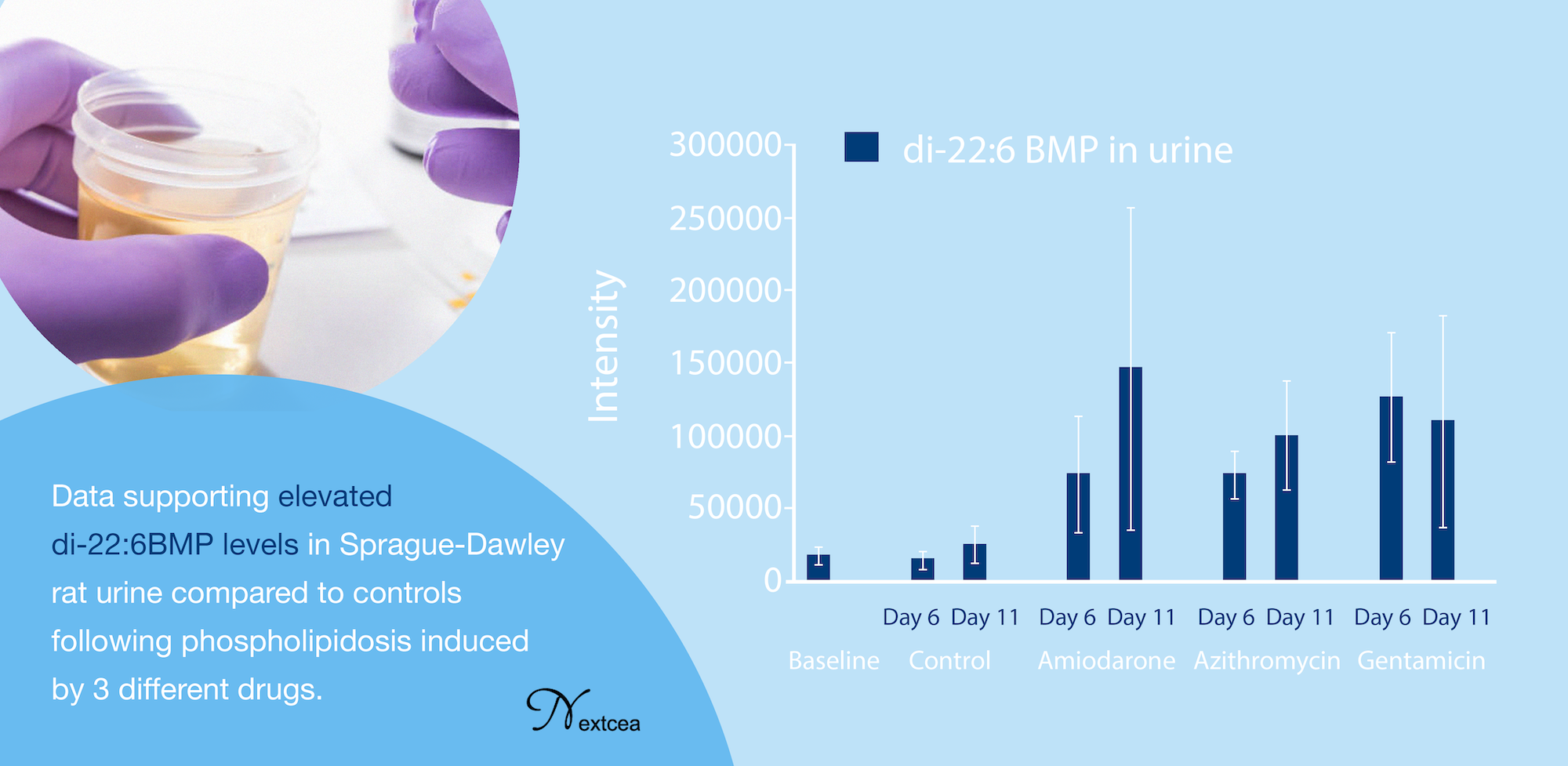

“The data provide evidence supporting the use of di-22:6-BMP as a urinary biomarker of PLD”
Mesens, et al. Toxicol Pathol. 2012;40(3):491-503.

“cholesterol sorting proteins NPC1 and NPC2, the amiodarone-induced traffic jam is thought to be located at the BMP level demonstrating its role in the mechanism of phospholipidosis-induction and its significance for use as a biomarker“
Thompson KL, et al. Int J Toxicol. 2012;31(1):14-24.
Providing validated LC-MS/MS DIPL Biomarker Quantitative Assay to manage uncertainty in drug safety better
Nextcea specializes in DIPL bioassay services for non-clinical and clinical studies. We provide GLP validated bioanalytical LC-MS/MS methods for measurement of non-invasive di-22:6-BMP in animal and human matrices (urine).

References
- Hsieh F., Tengstrand E. Detecting Phospholipidosis and Diagnosing Lysosomal Storage Disorders. US Patent 8,313,949,
Japanese Patent 5,702,363, and European Patent EP2419742. - Liu N., Tengstrand E., Chourb L., and Hsieh F. Di-22:6-bis(monoacylglycerol)phosphate: a clinical biomarker of drug-induced phospholipidosis for drug development and safety assessment. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 2014;279(3):467-476.
- Tengstrand E., Miwa G., and Hsieh F. Bis(monoacylglycerol)phosphate as a non-invasive biomarker to monitor the onset and time-course of phospholipidosis with drug induced toxicities. Expert Opinion in Drug Metabolism and Toxicology 2010; 6(5):555-570.
- Tengstrand-Baronas E., Lee J.W., Alden C., and Hsieh F. Biomarkers to monitor drug-induced phospholipidosis. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 2007;218:72-78.
- Thompson, K.L., Haskins, K., Rosenzweig, B.A., Stewart, S., Zhang, J., Peters, D., Knapton, A., Rouse, R., Mans, D., and Colatsky T. Comparison of the diagnostic accuracy of di-22:6-bis(monoacylglycerol)phosphate and other urinary phospholipids for drug-induced phospholipidosis or tissue injury in the rat. International Journal of Toxicology 2012;31(1): 14-24.
- Thompson, K.L., Zhang, J., Stewart, S., Rosenzweig, B.S., Shea, K., Mans, D., and Colatsky, T. Comparison of urinary and serum levels of di-22:6-bis(monoacylglycerol)phosphate as noninvasive biomarkers of phospholipidosis in rats. Toxicology Letters. 2012;213(2), 285-91.

 Non-invasive (urine)
Non-invasive (urine) Validated biomarker quantitated by LC-MS
Validated biomarker quantitated by LC-MS Assay sensitivity 96.7 and assay specificity 100
Assay sensitivity 96.7 and assay specificity 100